辛苦下载完ubuntu 11.04版本,为了安装它我花了大约半天的时间,事实上真的很痛苦,却只是因为一句配置参数的问题。。。
起初我用ultraiso的刻录到u盘进行安装,启动的时候显示syslinux的时候,就不动了。然后重进入windows系统,用ubuntu官网上的工具进行格式化u盘并安装,结果连syslinux都看不到,只有光标在一闪一闪的。开始以为ISO下载的有问题,于是到网上找了一下md5值,然后本地用PHP运行了一下md5_file计算了一下MD5值,结果与网上的一样,当时我就差点哭了。我RP没有这么差吧。
无意中在闲逛的时候发现了某篇文章(现在找不到了,误关闭了一下,原来只是改一下配置参数)
于是我重新用ultraISO把系统重新刻录到了U盘。然后到/syslinux/目录下,找到了syslinux.cfg,打开后把default vesamenu.c32这一行注释掉,重启选择U盘启动。
于是顺利的使用了ubuntu 11了。
OK,上一下截图。。。
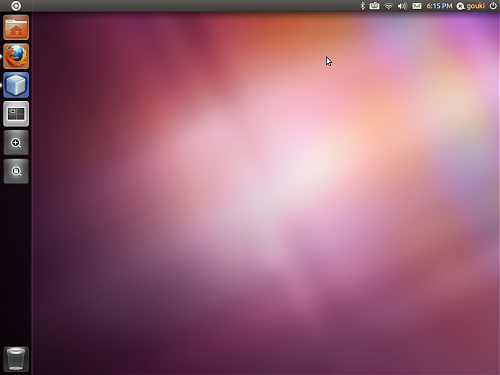
安装ubuntu 11.04成功
Submitted by gouki on 2011, May 3, 6:16 PM
终端服务器超出了最大允许连接数临时解决方法
Submitted by gouki on 2011, May 2, 7:23 PM
连接win的服务器的时候,如果非正常情况退出很有可能就会出现:“服务器超出了最大允许连接数”,这时候就比较痛苦了,如果临时需要改东西,而服务器上又运行着重要服务,这时候改也改不了了。又不能随便重启怎么办?以前自己的服务器我都是直接重启的,但是如果运行着重要的公司业务的话就不能这样折腾了。。。
这是找到的资料,先备份一下,以后可能会用的到,来源:http://www.zeali.net/entry/672
江湖救急的方法:
命令行运行 mstsc /console /v:服务器名或IP或域名:远程端口 。比如 mstsc /console /v:172.16.18.99:3389
但有时候这样运行之后仍然会出现“终端服务器超出了最大允许连接数”的错误信息,那样的话你可以尝试把 /console 参数换成 /admin 来连接。
附:
mstsc 语法 (Microsoft terminal services client)
mstsc.exe {ConnectionFile|/v:server} [/console] [/f] [/w:width /h:height]
mstsc.exe /edit”ConnectionFile”
mstsc.exe /migrate
mstsc参数
ConnectionFile 指定用于连接的 .rdp 文件的名称
/v:server[;port] 指定要连接的远程计算机
/admin 将连接到会话以管理服务器
/f 在全屏幕模式下启动“远程桌面”连接
/w:width 指定远程桌面窗口的宽度
/h:height 指定远程桌面窗口的高度
/public 在公用模式下运行远程桌面
/span 是远程计算机的高度和宽度与本地虚拟桌面相匹配,如有必要扩展到多个显示器。
若要扩展到多个显示器,所有显示必须具有相同的高度并垂直排列
/console 连接到指定 Windows 2000 Server 的控制台会话
/edit 打开指定的 .rdp 文件进行编辑
/migrate 将使用“客户端连接管理器”创建的旧版连接文件迁移到新的 .rdp 连接文件中
沙尘暴?
Submitted by gouki on 2011, May 1, 10:29 PM
五一,本来是个好日 子,然而晚上鼻子中闻到的都是一股尘土的味道,一下子什么心情都没有了。
于是心里特别为那些生活在北方地区的人感到可怜,他们其实比我们更痛苦啊,我们只是偶尔发生这样的事情,他们一年中却是有小半的日子都会有这种感觉。
早日希望沙尘暴过去。


顺便祝福那些在国际劳动节还在加班的朋友们节日快乐。
最后吐槽一下,我的组织关系在家里,差点居然没了。老爸去帮我问了几次,工作人员都说不知道没看过,后来直到发脾气了,才肯找。当然最后是找到了。于是有时候想想,为什么家乡的发展总是那么慢,与工作人员人的态度还是有关系的。非利益部门就是在撞钟过日子,让别人会怎么样想呢?
ubuntu 11.04
Submitted by gouki on 2011, April 30, 11:17 PM
Ubuntu 11.04下载完啦,准备有空在笔记本上折腾一下,反正笔记本目前电池也坏了。也不在乎它耗电量是多还是少了。
只是电脑里的东西备份出来的时候会浪费我的移动硬盘很大的空间啊。心还是很痛的。。。
100多G就这么没了。
想装ubuntu主要是界面比以前好看多了,而且,现在WEBQQ也支持讨论组了,所以,就更加可以用了(firefox 4也支持把某个TAB PIN成一个APP【说法太烂了我,其实就是pin as app tab】)
尝试喽。让老婆用台式机吧。黑黑
QQ硬盘
Submitted by gouki on 2011, April 30, 1:22 AM
在微博上无意中看到以下内容:
QQ硬盘Beta2抢先试用版发布啦!只要你是QQ会员,获取体验资格后即可使用该版本http://url.cn/1DUU6Z 。QQ硬盘Beta1内测用户不妨重新登录QQ,会有惊喜哦!
于是尝试了一下,目前没有看到有什么新的特色,因为没有什么特别的同步功能(当然我在猜想,如果真的QQ硬盘出来后,一旦有了同步,那就是说所有的QQ可能就会被自动安装在QQ硬盘里,真的是随处可聊了。随便说说而已。因为如果真的QQ硬盘能够同步了,那其他软件厂商一定会痛苦万分)
毕竟QQ一直在做这种,走自己的路让别人无路可走的事情。
这次所谓的第二版,更新了一些内容:
主要更新:
- QQ硬盘界面优化,带给您更顺畅的体验。
- 全新的存储架构,让服务更加稳定、传输更加迅速。
- 新增精简模式,上传更方便。
- 文件夹上传的逻辑优化,上传更加快捷。
- 多线程上传、下载操作优化。
- 任务列表优化,传输操作一目了然
- 任务支持拖拽上传下载,更便捷
一看这种样子就是明显的不支持WIN以外的系统(可惜还是没有同步功能)
运行了之后,把QQ网络硬盘里的东西转移到了QQ硬盘。
QQ的硬盘系列让我很头晕 ,网络硬盘,QQ硬盘,随身盘 。。。啥时候会全部合并呢?天知道
随便用用吧,不过好象仅限会员。

